“INSAT-4B has been disposed of after the mission (PMD) at the end of its life on January 24, 2022 after decommissioning to UN compliant and Inter Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee ,iadc) recommended space debris mitigation guidelines,” ISRO said.
INSAT-4B was launched on 12 March 2007 for DTH and other communication services. After completing nearly 14 years of on-orbit operations, INSAT-4B’s C band and Ku band payload services were transferred to other GSATs before the commencement of post-mission disposal.
“According to the IADC space debris mitigation guidelines, at the end of its life, a live The object must be raised into a nearly circular orbit above the GEO belt to prevent its orbit from falling back into the GEO protected zone within 100 years of re-orbiting. In this case, the required minimum orbit increase was 273 km and this is achieved through 11 re-orbiting maneuvers executed during 17-23 Jan 17-23,” ISRO said.
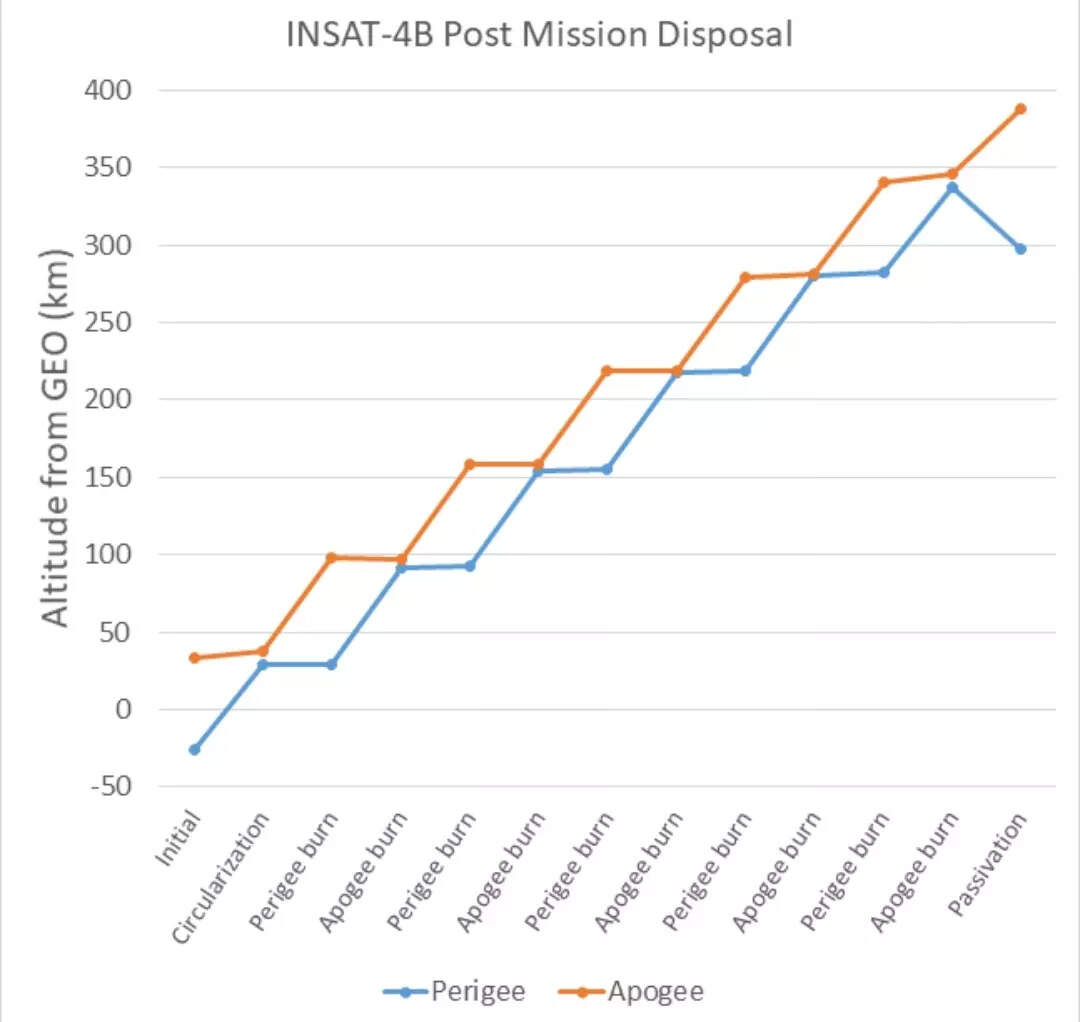
The space agency said that the aim of the first maneuver was to go round the orbit. Later re-circulating maneuvers were executed at perigees (closest to Earth) and the apogee (farthest) alternately form intermediate orbits near circular ones.
“All maneuver plans were checked to ensure that there was no close approach or risk of collision between any other space objects (active satellites and space debris) in the near future. On January 24, the remaining propellant venting and The power inactivation activities were done to reduce the risk of post-mission breakdown before finally deactivating the satellite,” ISRO said.
This telecommunications intensive operation, it said, 70-74 . was executed between degree prior longitude zone to avoid radio frequency interference with other operational GEO satellites.
“INSAT-4B is the 21st Indian Earth satellite to undergo PMD. The propellant required for such re-orbiting was included in the initial fuel budget as a part of standard exercise in ISRO’s GEO mission plan. Finally The achieved orbit is about 340 km above. “The altitude of GEO is in full compliance with IADC guidelines for space debris mitigation of GEO objects,” ISRO said.
The successful PMD marks yet another effort by ISRO to ensure the safety and stability of outer space operations through careful planning and flawless execution.
,