Highlight
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced its monetary policy.
- RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das has decided not to make any change in interest rates.
- There are no significant signs of an imminent turnaround in economic growth.
RBI Monetary Policy: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced its monetary policy, and RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das has decided to keep interest rates unchanged in line with expectations, as inflation remains high and there are no significant signs of an imminent turnaround in economic growth. are not. Read on to know about monetary policy, its objectives and policy stand, its various instruments and monetary policy projections.
What is a monetary policy?
Monetary policy is the process by which a central bank, like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), affects the supply and demand of money in an economy to promote economic growth and stability. The RBI uses a number of tools to achieve these goals, including setting interest rates, changing reserve requirements and engaging in open market operations.
RBI Monetary Policy 2022: Objectives and Policy Stand
Monetary policy aims to achieve the medium-term target of 4% for consumer price index (CPI) inflation with a range of plus or minus two percent. The current monetary policy follows a accommodative stance due to the economic slowdown affected by the Covid-19. This was the main reason why the MPC reached a consensus that the policy repo rate should remain unchanged.
From June 2022, it is expected that this economic policy stance will become neutral, but rates will remain low to maintain inflation levels and keep them at 4% (+/- 2%) by the end of FY 2022 .
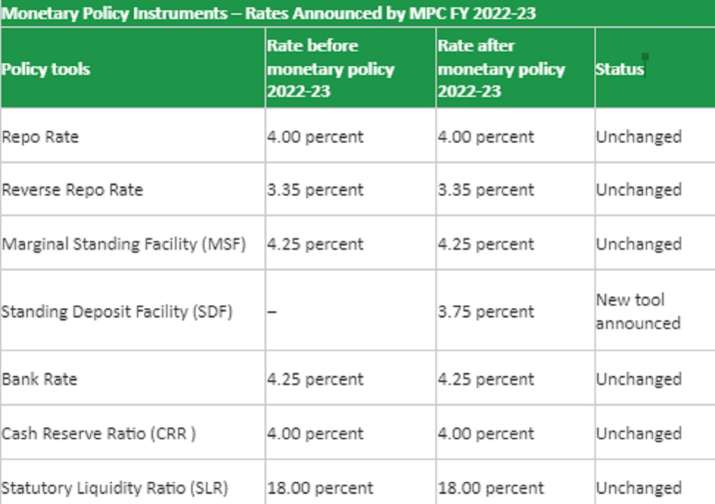
Major Instruments of Monitoring Policy 2022-23
Even though the monetary policy instrument remains unchanged, a new policy instrument has been added called the Fixed Deposit Facility. SDF is used to reduce liquidity because the liquidity adjustment facility does not provide adequate discounting. The introduction of the SDF is expected to harmonize the operational framework of monetary policy by matching absorption facilities with marginal standing facilities at opposite ends of the liquidity adjustment facility corridor.
Monetary policy instruments 2022 remain unchanged
Repo rate is the interest rate at which banks borrow money from RBI. The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has kept the repo rate unchanged at 4%. Reverse repo rate refers to the interest rate at which banks deposit their surplus funds with the RBI. The reverse repo rate remains unchanged at 3.35 per cent.
The marginal standing facility, bank rate, cash reserve ratio and statutory liquidity ratio were also kept unchanged. The decision was taken unanimously by a six-member panel. The central bank also decided that it will continue its accommodative stance as long as it is necessary to sustain growth on a sustainable basis and inflation remains within the target range of 2-6 per cent.
monetary policy projections
Due to the current policy, the MPC lowered GDP growth expectations for fiscal year 2022-23 from 7.8% to 7.2%. Based on the recommendation of its experts, the RBI is shifting to a more conservative monetary policy by projecting annual inflation at 5.7% instead of the initial projection of 4.5%.
conclusion
While the RBI’s monetary policy is generally lenient, it aims to support growth over inflation. This year, the Reserve Bank of India wants to adopt a more neutral policy stance and prioritize price stability.
Read also: RBI is considering setting up a fraud registry to check banking frauds
Read also: RBI lifts ban on American Express; Allows new domestic customers to join